| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 파이썬 재귀함수
- 프로그래머스 파이썬
- 프레임워크란?
- 양과늑대
- 카카오 파이썬
- 부스트캠프 회고
- 파이썬 카카오코딩테스트
- Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix
- 프로그래머스
- 도커연결오류
- 라이브러리란?
- 부캠
- 파이썬
- 파이썬 양과늑대
- 프로그래머스 레벨2
- 네이버 부스트캠프
- 프로그래머스LEVEL1
- 파이썬 프로그래머스
- 부스트캠프
- level1
- 카카오 코딩테스트
- 프로그래머스 양과늑대
- docker시작하기
- 카카오코테
- 도커오류
- 코딩테스트
- 프로그래머스 레벨1
- 프로그래머스 레벨3
- 카카오코딩테스트
- 부스트캠프AITech
- Today
- Total
코린이의 공부일기
[Boost Camp] 1 WEEK . Days- Numpy의 기초 본문
강의제공 - boost camp
1. Numpy란 ?
- Numerical Python
- 파이썬의 고성능 과학 계산용 패키지
- Matrix와 Vector와 같은 Array연산의 사실상 표준
- 일반 List에 비해 빠르고, 메모리 효율적
- 반복문 없이 데이터 배열에 대한 처리를 지원
2. Numpy 호출방법
import numpy as np
-일반적으로 numpy는 np라는 별칭을 이용해 호출함
3.Numpy 생성
print(test_array=np.array(["1","4",5.0,8],float)) #float로 선언
print(type(test_array[3]))*출력
array([1 . ,4 . ,5 . , 8.])
numpy.float64
- numpy는 하나의 데이터type만 배열에 넣을 수 있음(data type을 정해줄 수 있다.)
4.numpy와 List의 차이
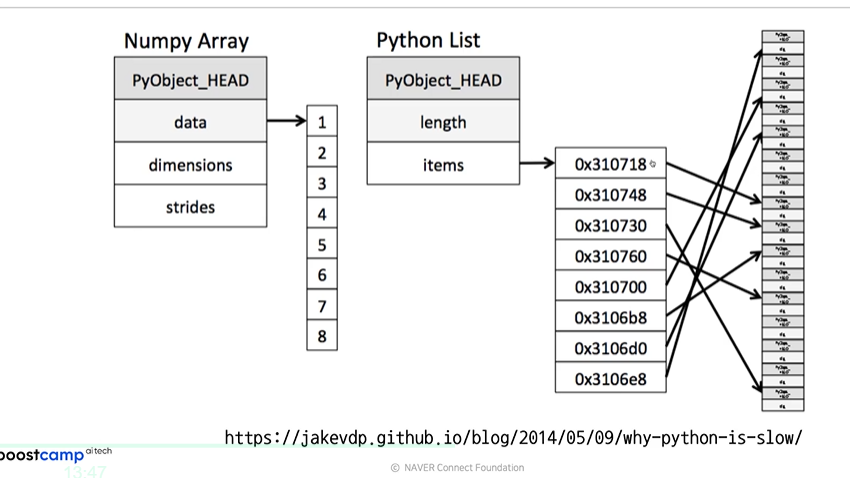
- Numpy는 차례대로 값이 들어감.
- 메모리의 접근성이 Numpy가 더 좋다.
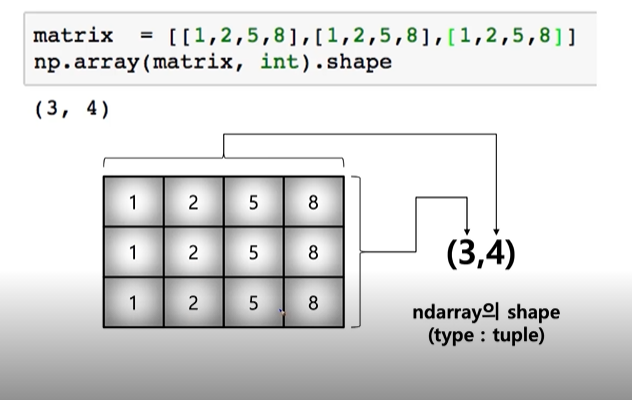
5. Numpy의 용어
-shape: numpy array의 dimension구성을 반환
- Array shape(vector)

- Array shape(matrix)
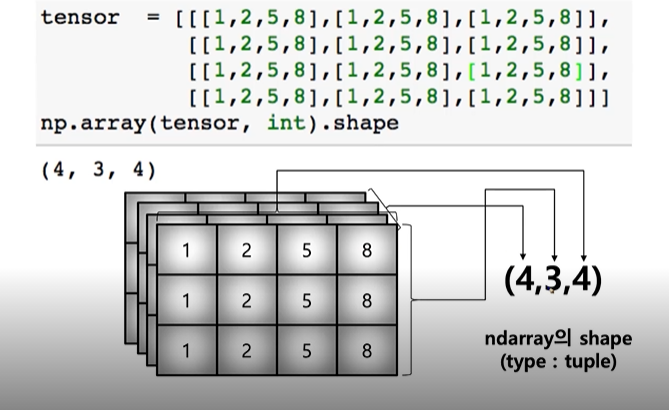
- Array shape(3rd order tensor)
- dtype: numpy arrat의 type을 반환
- ndim:number of dimensions
- size: data의 개수 ex? (4,3,4) ->원소 48개
test_array=np.array([1,4,5,8],float)
print(test_array)
print(type(test_array[3])) #Float Type으로 자동 형변환 실시
print(test_array.dtype) #Array(배열) 전체의 데이터 Type을 반환
print(test_array.shape) #Array(배열)의 shape을 반환#출력
[1. 4. 5. 8.]
<class 'numpy.float64'>
float64
(4,)
*여기서 중요한 것 !- numpy는 list와 달리 dynamic supporting을 지원하지않음 즉, 무조건 같은 type형만 nd.array에 저장이 가능 , numpy는 data타입을 지정해줄 수 있음
6. Array nbytes
-nbytes- ndarray object의 메모리 크기를 반환함
np.array([[1,2,3],[4.5,"5","6"]], dtype=np.float32).nbytes32bits = 4 bytes -> 6*4 bytes =24bytes
- 메모리를 적게 소요하고 있는게 더 좋은 것은 아님.
*Hadling shape
7. reshape
- Array의 shape의 크기를 변경함, element갯수는 동일하다.
test_matrix=[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,5,8]]
np.array(test_matrix).shape*출력 (2,4)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(8,)#출력 array([1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8])
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(-1,2).shapereshape(-1, 지정값)
-1: size을 기반으로 row개수 선정
7.flatten
- 다차원 array를 1차원 array로 변환
test_matrix=np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 5, 8]])
test_matrix.flatten()#출력
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8])
8. indexing for numpy array
-list와 달리 이차원 배열에서 [0,0] 표기법을 제공함
-matrix일 경우 앞은 row뒤는 column을 의미
a=np.array([[1,2,3],[4.5,5,6]],int)
print(a[0,0])#출력 0
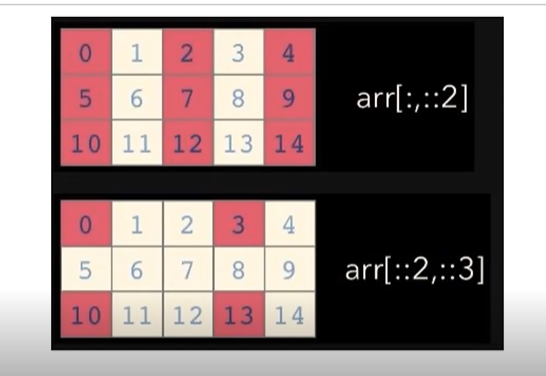
9. slicing for numpy array
- list와 달리 행과 열 부분을 나눠서 slicing이 가능함
- matrix의 부분 집합을 추출할 때 유용함
a=np.array([[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10]],int)
print(a[:,2:]) #전체 row의 2열 이상
print(a[1,1:3]) #1 row의 1열~2열
print(a[1:3]) #1row~2row의 전체#출력
[[ 3 4 5] [ 8 9 10]]
[7 8]
[[ 6 7 8 9 10]]
10. arange
- array의 범위를 지정하여, 값의 list을 생성하는 명령어
np.arange(30).reshape(5,6)#출력
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17],
[18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29]])
11. identity
- 단위 행렬을 생성함 n-> number of rows
np.identity(n=3,dtype=np.int8)#출력
array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]], dtype=int8)
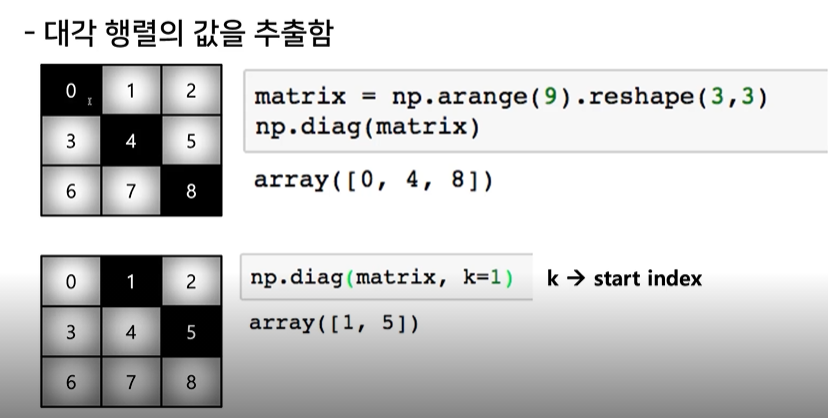
12. diag
- 대각 행렬의 값을 추출
13. random sampling
- 데이터 분포에 따른 sampling으로 array을 생성
- random.uniform(시작값, 끝값, data의 개수)
np.random.uniform(0,1,10).reshape(2,5)#출력
array([[0.47420167, 0.52110346, 0.07759909, 0.36682082, 0.06365799],
[0.38307182, 0.56236159, 0.69351393, 0.23874585, 0.03644417]])
*operation functions
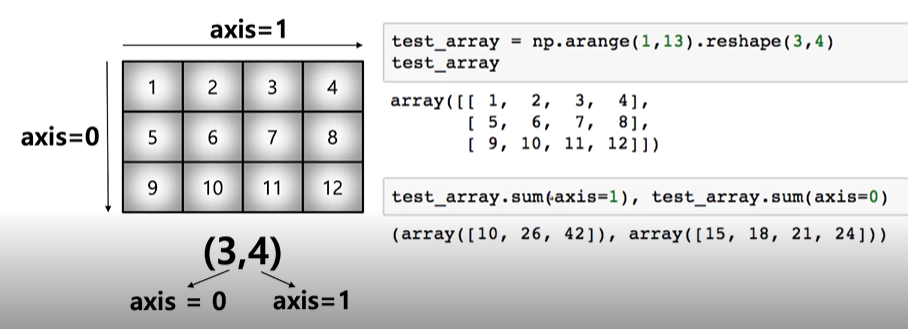
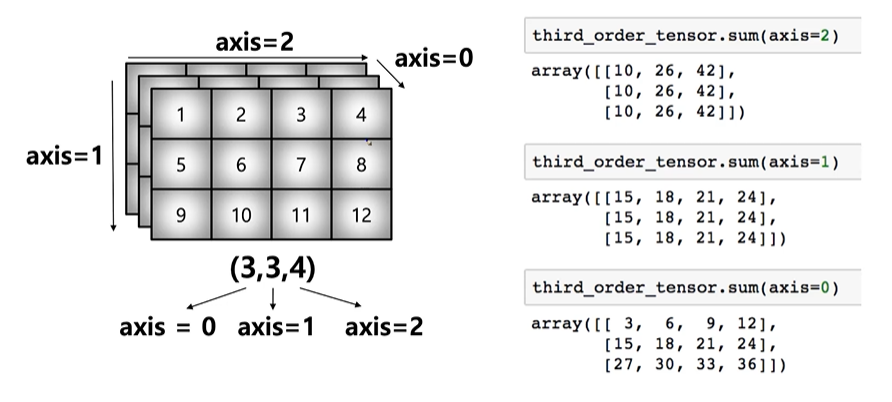
14. axis
- 모든 operation function을 실행할 땨 기준이 되는 dimension 축
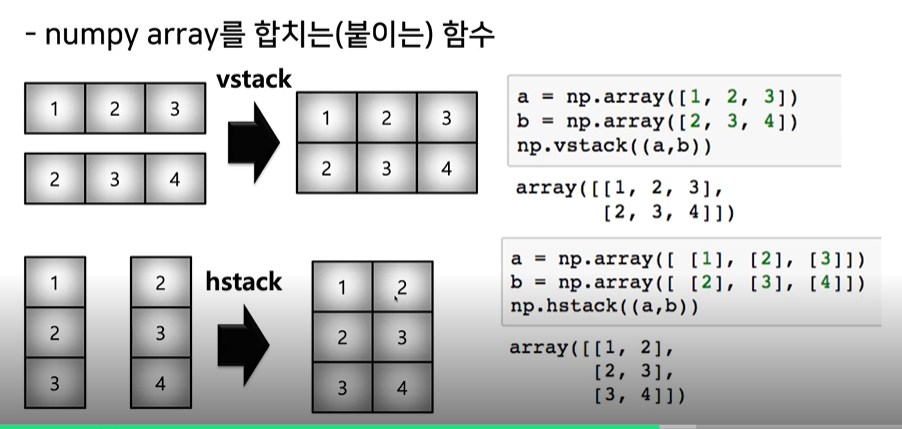
15. concatenate
- numpy array을 합치는(붙이는 )함수
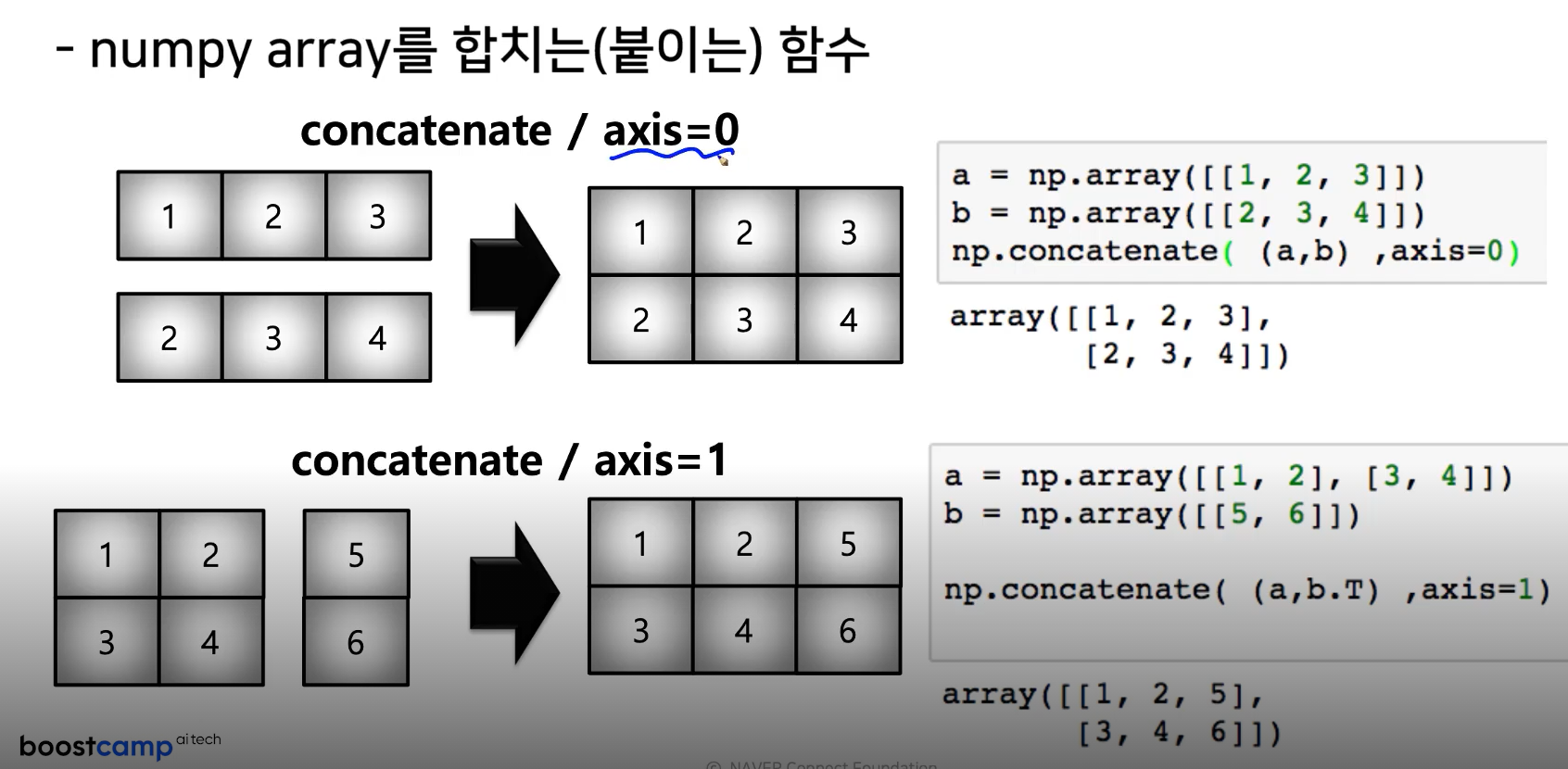
a=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
b=np.array([5,6])
b=b[np.newaxis, :]
np.concatenate((a,b.T), axis=1) #열 기준으로 합치기#출력
array([[1, 2, 5],
[3, 4, 6]])
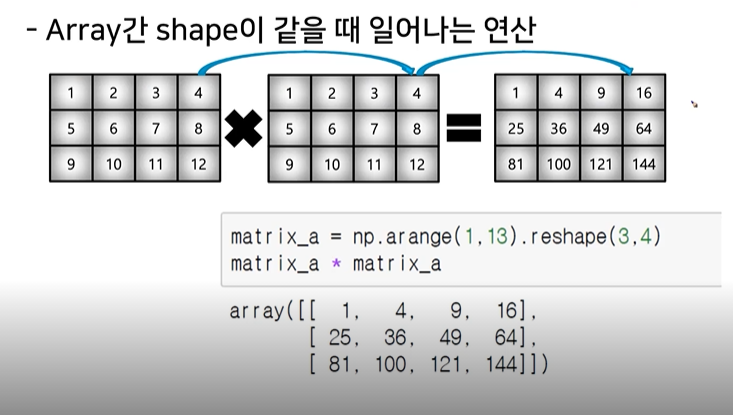
16. Element-wise operations
- array들 끼리의 크기가 같다면 element_wise operations으로 원소끼리 연산
- 곱셈, 뺄셈, 덧셈 모두 원소간의 연산
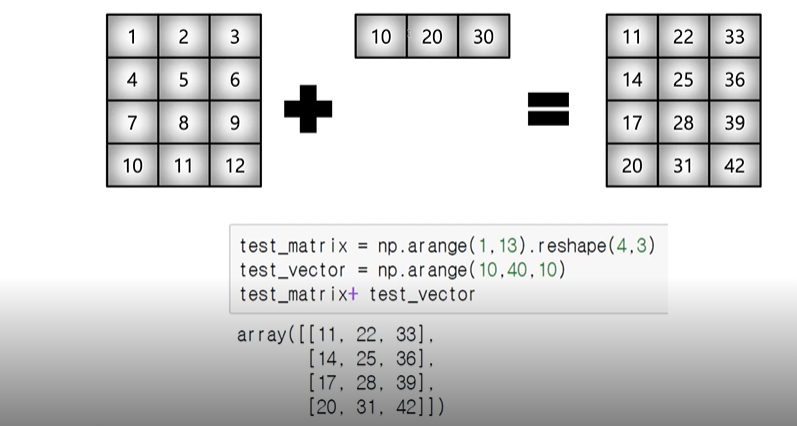
17. broadcasting
- shape이 맞지 않은 연산일 경우, 둘 간의 shape을 맞추어 연산하는 것
18.comparison operation 1
- numpy는 배열의 크기가 동일 할 때 element간 비교의 결과를 Boolean type으로 반환
test_a=np.array([1,3,0],float)
test_b=np.array([5,2,1],float)
test_a>test_b#출력
array([False, True, False])
(test_a>test_b).any()
#출력
True
(test_a>test_b).all()#출력
False
19. np.where
- where(condition, TRUE, FALSE)
a=np.array([1,3,0],float)
np.where(a>0,3,2)#출력
array([3, 3, 2])
'BOOST CAMP_정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Boost Camp] 1WEEK.5Days -RNN (0) | 2021.08.09 |
|---|---|
| [Boost Camp] 1WEEK.4Days CNN의 기본 (0) | 2021.08.09 |
| [Boost Camp]1WEEK. 4Days-1 확률론의 기초 (0) | 2021.08.08 |
| [Boost Camp] 1WEEK. 3Days-2 경사하강법 (0) | 2021.08.08 |
| [Boost Camp] 1WEEK . 3Days- 1. 벡터의 기초 (0) | 2021.08.08 |




